USE-CASES
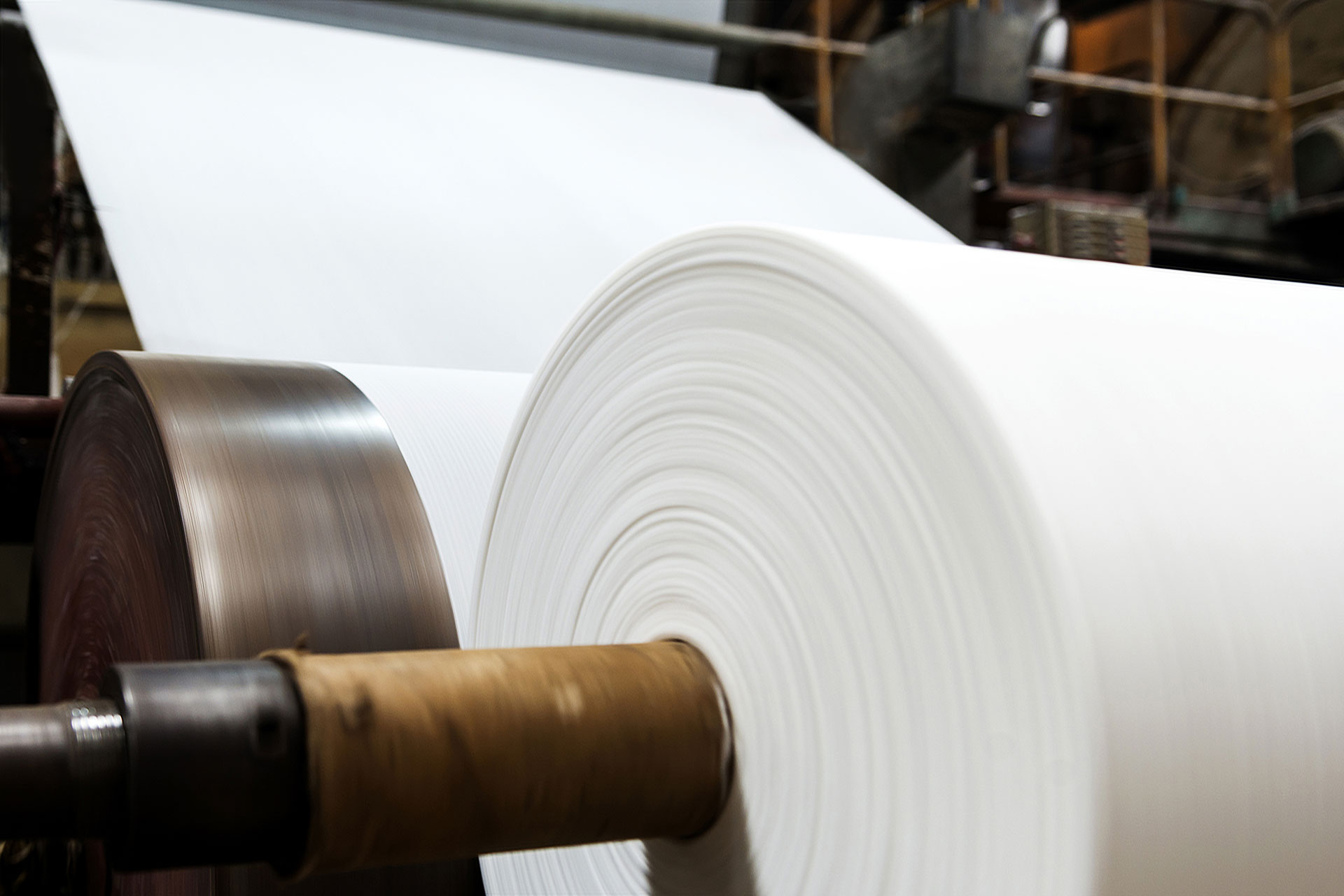
PAPER INDUSTRY
Especially in paper production and processing, controlled air humidification is of particular importance. Since paper very easily absorbs and emits moisture, swelling and shrinking as well as electrostatic charges can be efficiently avoided under a constant climate. A smooth finishing process (printing, cutting, refinement etc.) is therefore guaranteed.

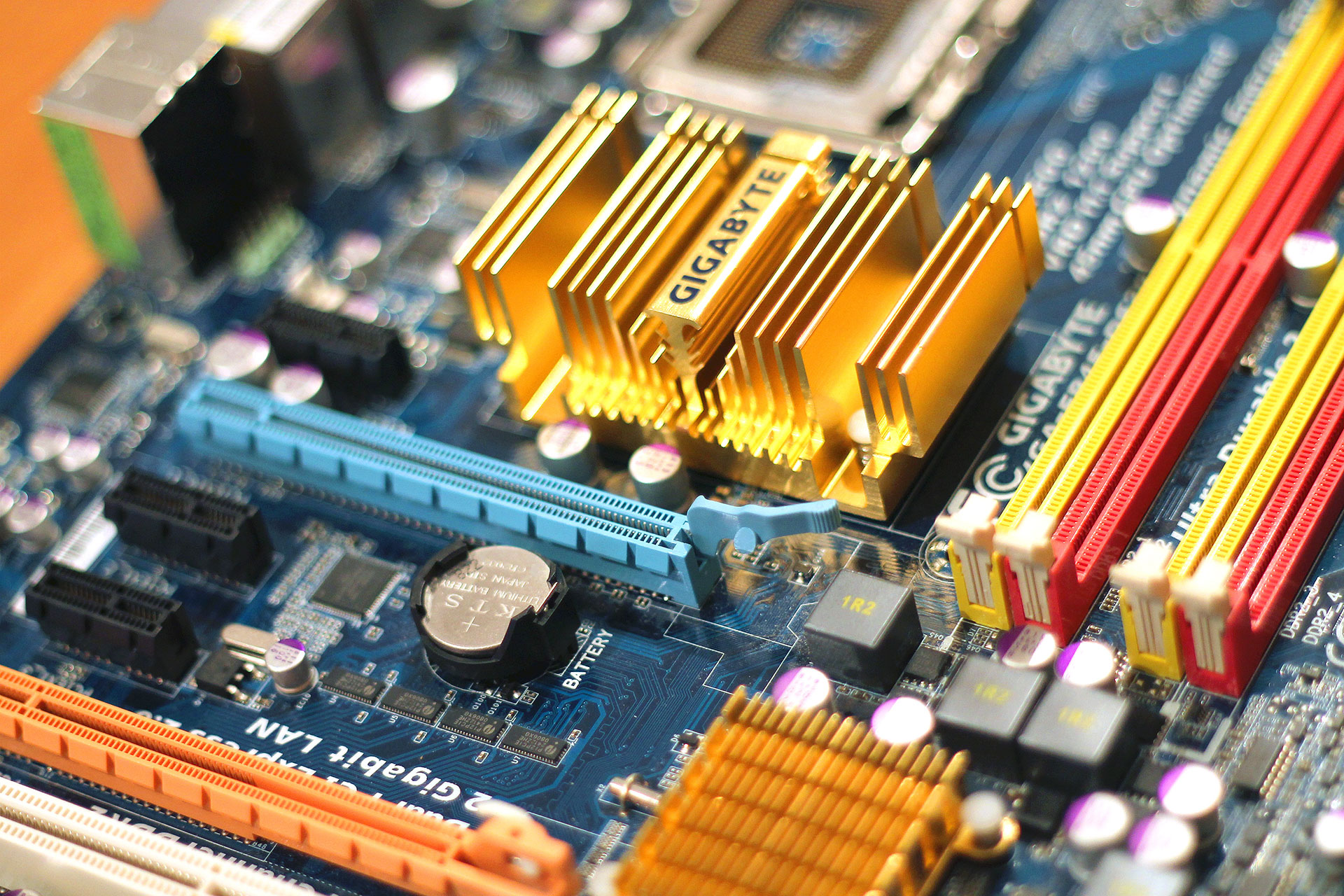
ELECTRONIC INDUSTRY AND DATA CENTERS
High temperatures, electrostatics and dust are known to be among the biggest problem areas in the electronics industry and data centers. Through well-targeted application of finest water particles (aerosols) a cost-efficient additional reduction of the room temperature can be achieved, electrostatic can be reduced to a minimum and additionally undesirable dust can be bound.
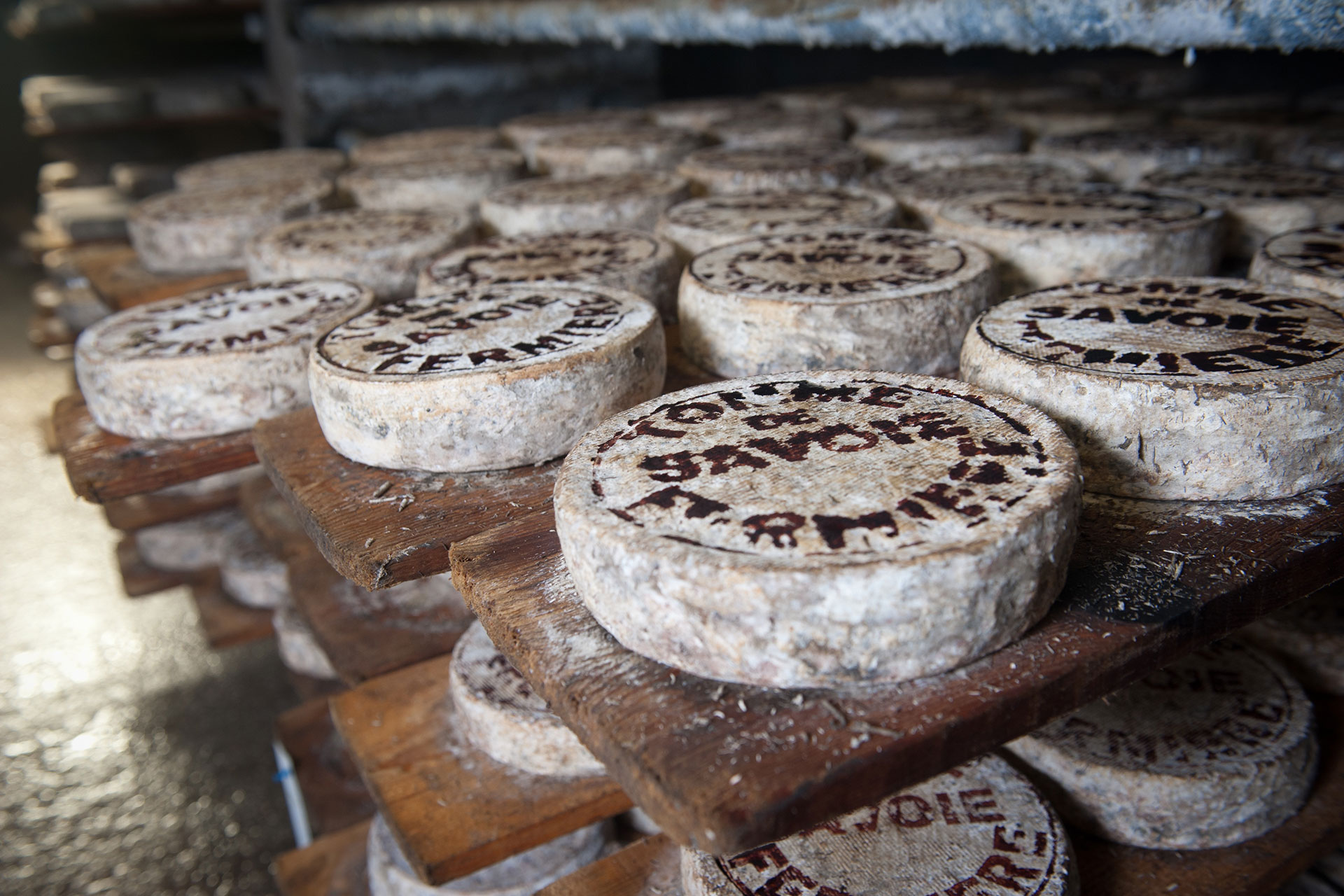
STORAGE OF CHEESE
Cheese needs a special microclimate during the ripening process. A component of this microclimate is, of course, also an appropriate humidity, which affects not only the taste of the finished product but also the consistency and as a consequence the weight.
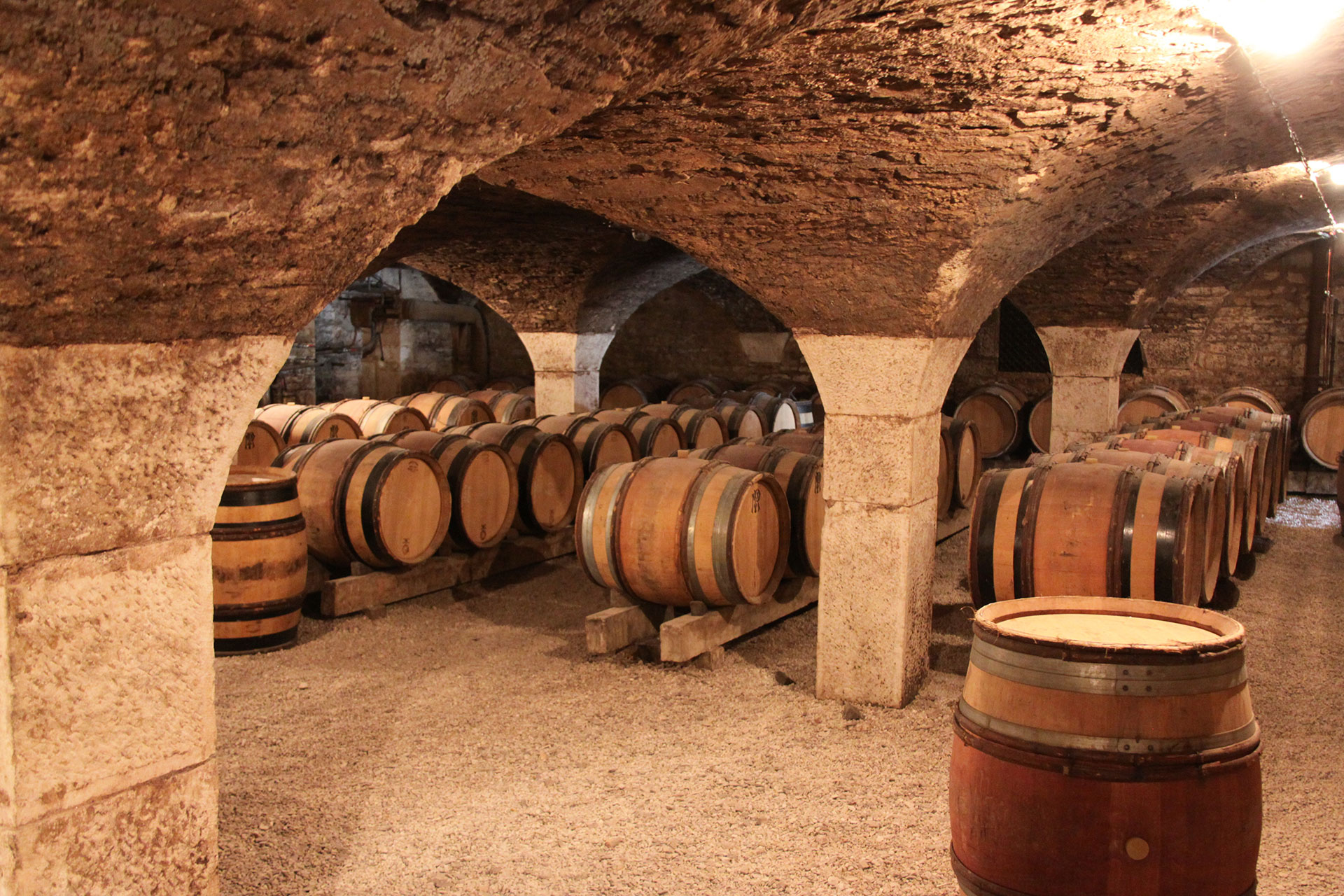


STORAGE OF WINE
Similar to cheese, wine also needs a constant climate during the ripening process and storage. In order to avoid corks to shrink or mold an ideally adjusted humidity is 85%. For the aging and storage in barrique barrels 75% is ideal since the wood does not form a dry crack and thus the diffusion of the wine through the barrels can be significantly reduced.
FOOD INDUSTRY
For a variety of foodstuff a controlled humidity guarantees both freshness and quality during the production and storage process. In addition weight losses can be avoided and targeted maturation processes can be set.


WOODWORKING INDUSTRY
In order to guarantee a consistent quality with regard to dimensional and fitting accuracy in the processing of wood a precisely set humidity is essential. Both the swelling of the wood at too high as well as distortion or cracking at too low atmospheric humidity can be effectively eliminated.
DUST BINDING
Increased dust formation in rooms can be effectively reduced by air humidification systems. The water particles in the air bind the dust and cause it to fall to the ground as a result of the concomitant “weight gain”. The result is a cleaner climate and the avoidance of dangerous dust explosions.


TEXTILE INDUSTRY
Using the right air humidification in the production process of textiles can effectively prevent problems in the yarn processing (yarn breakage) as well as possible electrostatic charges; important aspects in ensuring a smooth production.
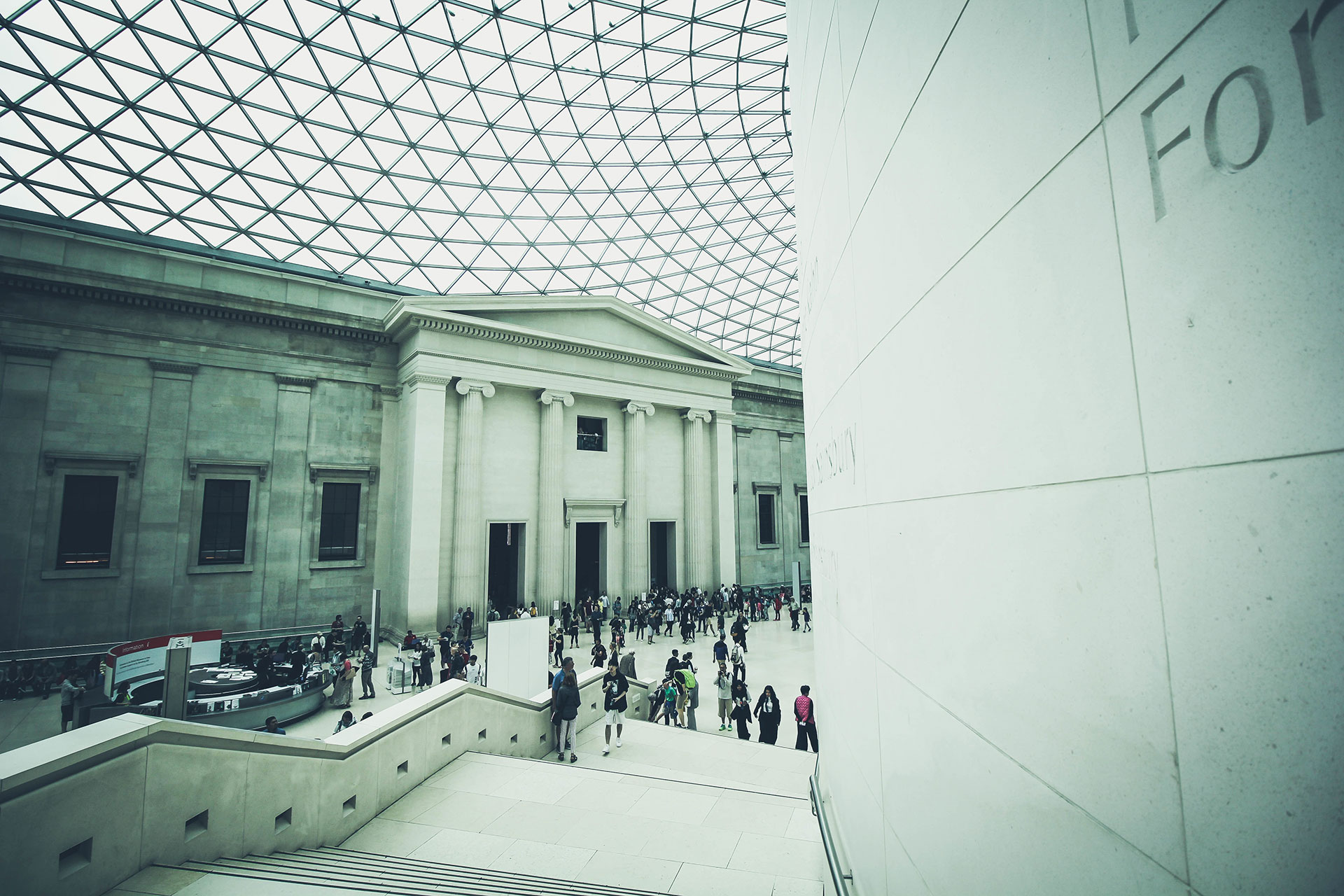
MUSEUMS
Objects exhibited in museums are often sensitive to changing climatic conditions. While too dry air results in objects being cracked and porous, too moist air also causes irreversible damage. With a correctly adjusted humidity exhibits are protected, room climate is improved and possible electrostatic charges and subsequent dust accumulation are reduced.
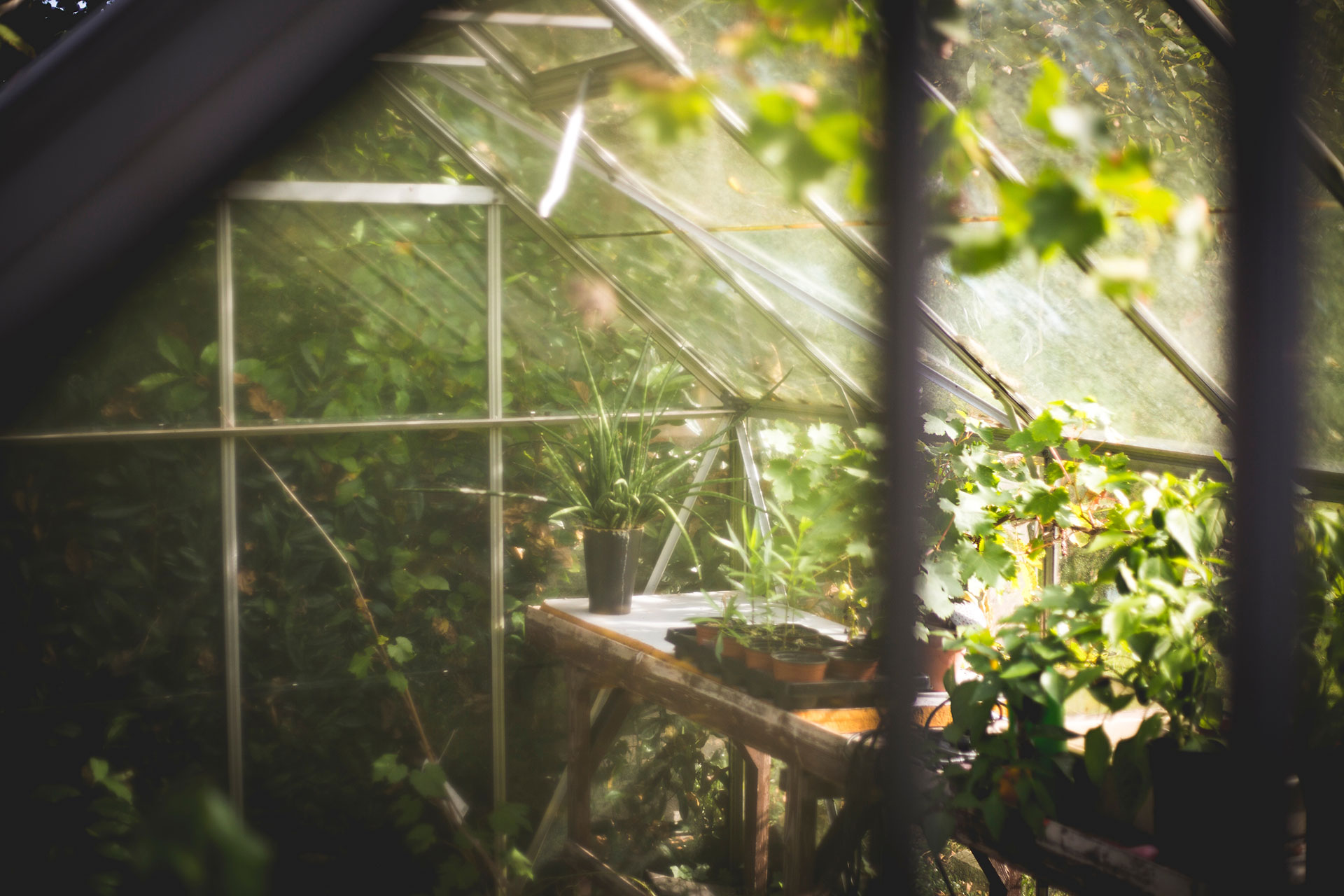


GREENHOUSES, TROPICAL PLANTS AND ZOOLOGICAL GARDENS
Air humidification systems in greenhouses, tropical plants and zoological gardens guarantee a constant climate control for plants and animals. In addition to the situational reduction of room temperatures of up to 7°C without additional energy expenditure the extremely fine spray mist can be used to achieve a high degree of humidity without causing a feeling of wetness.
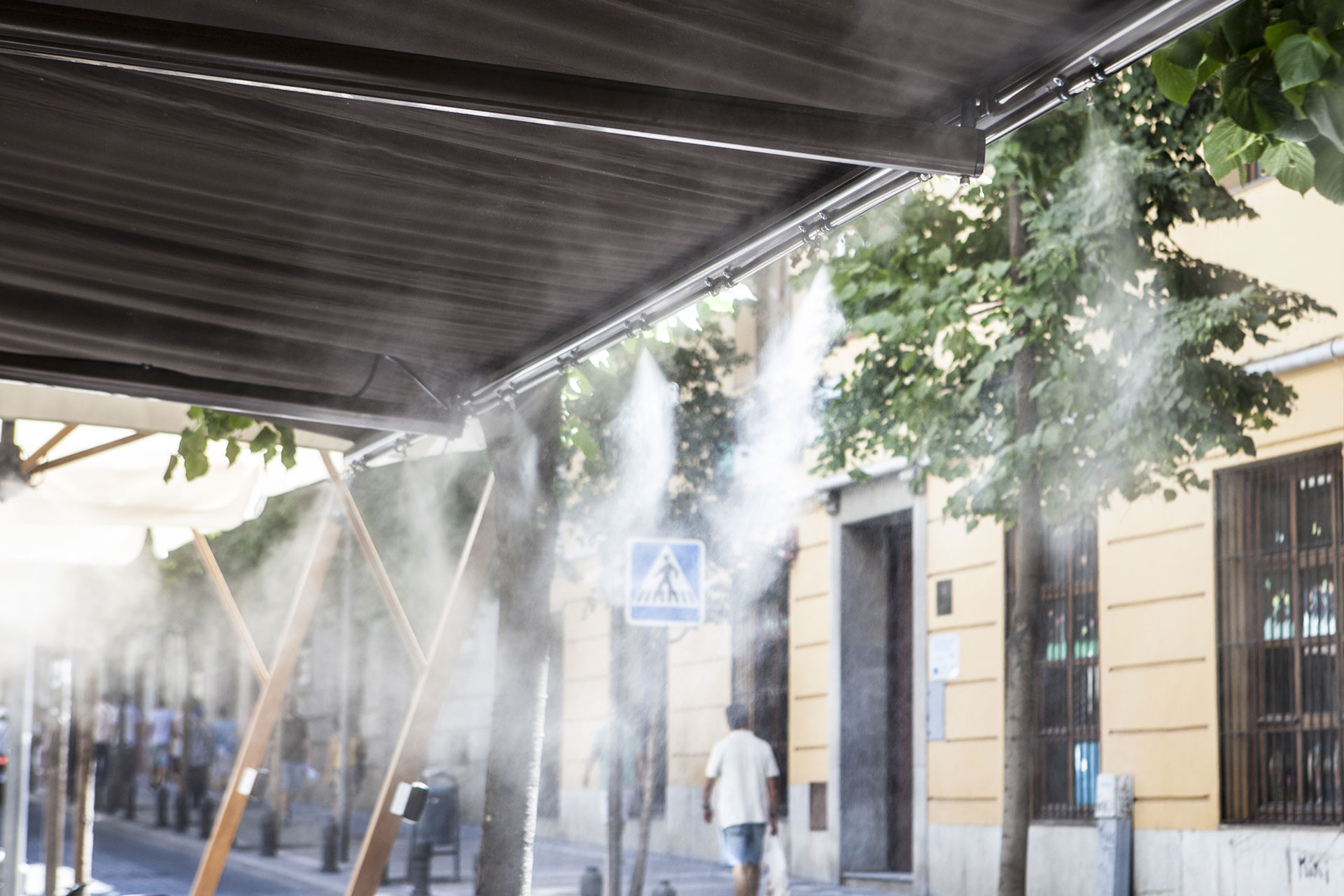
COOLING OUTDOOR AND INDOOR
More often air humidification systems are used to either support air conditioning systems or even replace them. Through the complete absorption of the microfine water droplets in the air heat is extracted from the room whereby a cooling of up to 7°C can be achieved. The principle of adiabatic evaporation cooling is becoming increasingly popular in the gastro area.
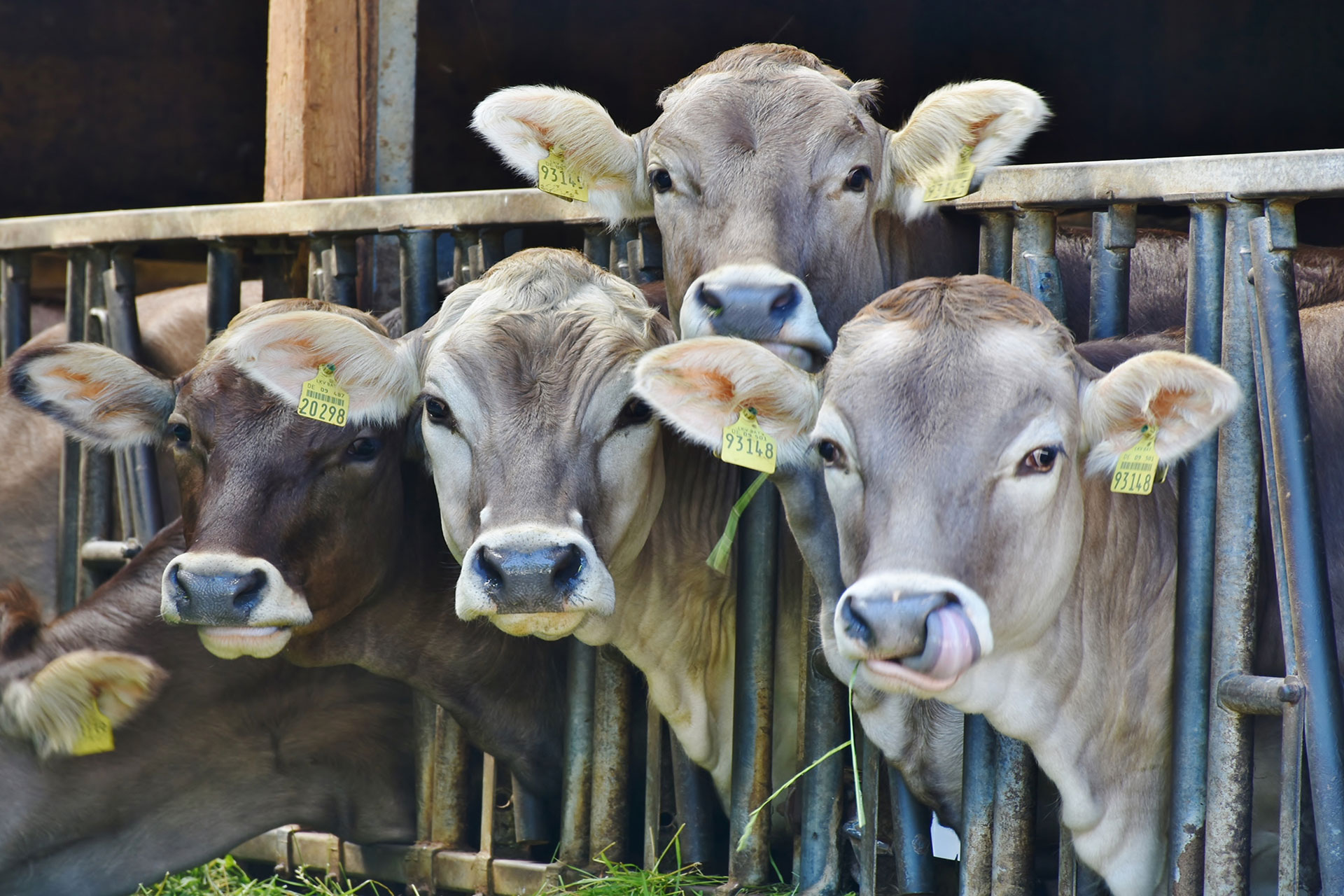


FACTORY FARMING
The use of humidification systems is unavoidable in animal breeding and fattening plants to ensure the right environmental conditions as a basis for the welfare of the animals and thus to keep health, yield and quality constant. Adiabate cooling protects the energy balance, dust particles and odors are significantly reduced and the addition of hygienic substances prevents the spread of diseases.